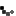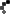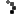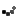Moorish architecture is named after the Moors, North African people who conquered the Iberian Peninsula in the begining of the 7th century. The Moors controlled what is now Spain and Portugal.
The Moors were influenced by the Islamic architecture that developed in the Middle East. Althoug mosques are the most common examples of Moorish architecture, motifs spread to the design of homes and places of businesses. One of the most famous examples of Moorish architecture, the Mezquita or Grand Mosque of Cordoba.
Moorish architecture is a variation of Islamic architecture. There are many motifs or repeated patterns: different styles of arches, calligraphy, vegetative design, and decorative painted tilles.
One of the most distinguished caracteristics of Moorish architecture is the plain exterior of a structure with a richly decorated interior. Elements of nature always included in the buildings were courtyards with lush gardens, fountains, reflecting pools and landscapes. The climate of the region influenced the building materials used: tile, marble, adobe brick, clay and plaster. All these materials would stay cool in the heat of the summer. The Koran forbids the copying of natural forms so instead craftsmen used stars, crescents, crosses, hexagons and octagons. These geometric shapes and patterns were created in wood, plaster, tile and textile design.